How to Read Cummins Fault Codes?
Cummins engines are widely used in heavy-duty trucks, construction machinery, generators, and marine vessels. When the “Check Engine” light comes on or performance issues occur, reading and correctly understanding the fault codes is the first step to quickly identifying the problem, avoiding blind parts replacement (saving costs), and restoring normal operation of the equipment. So, how to read Cummins fault codes? Don’t worry, in this article, we’ll explain everything in detail. Let’s get started!
Part 1. What Are Cummins Fault Codes?
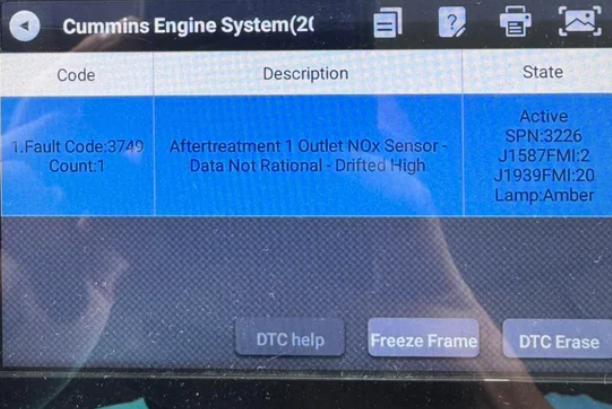
Fault codes (DTC, Diagnostic Trouble Code) are error or anomaly logs recorded by the Engine Control Module (ECM) to identify abnormal systems or sensors. Modern Cummins systems support both the traditional “Fault Code ####” display and the SAE J1939-based SPN/FMI (Suspect Parameter Number / Failure Mode Identifier) format.
Purpose: Fault codes typically indicate the affected system (such as fuel, intake, cooling, electrical, or data link) and come with different severity levels, including warning, derate, or shutdown. For a complete and accurate explanation of any fault code, Cummins INSITE/FIS software or the corresponding engine technical manual should be used.
Part 2. 4 Ways to Read Cummins Fault Codes
There are several ways to retrieve Cummins engine fault codes, depending on the vehicle model, engine generation, and available diagnostic equipment. Below are the most common and practical methods:
1. Dashboard Flash Codes (MIL / Check Engine Light)
On older Cummins-equipped vehicles, you can access basic fault codes without external tools. By pressing a specific button or cycling the ignition key in a certain sequence, the Check Engine light or Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will flash in patterns. Each sequence of flashes corresponds to a fault code number.
- Pros: Quick and requires no special tools.
- Cons: Limited to older models; codes are basic and may not provide full diagnostic details.
2. Cummins INSITE + Fault Information System (FIS)
This is the official and most accurate diagnostic method recommended by Cummins.
INSITE software connects to the ECM and provides:
- Active and inactive (historical) fault codes
- Freeze frame data (engine conditions when the fault occurred)
- Step-by-step troubleshooting recommendations
- Ability to clear codes after repair
FIS (Fault Information System) complements INSITE by offering authoritative explanations of each code, probable causes, and repair procedures.
For precision and reliability, INSITE + FIS is the gold standard for Cummins diagnostics, especially in professional fleet maintenance or repair shops.
3. Professional Diagnostic Tools / OBD-II / J1939 Scanners
Modern Cummins engines also support industry-standard protocols like OBD-II (light/medium-duty applications) and J1939 (heavy-duty). Using a compatible scan tool, you can:
- Read SPN/FMI codes (Suspect Parameter Number / Failure Mode Identifier)
- Clear stored fault codes
- View live engine data streams and historical event logs
- Perform basic tests depending on tool capability
These commercial diagnostic tools are widely used outside Cummins-authorized networks and are suitable for workshops and fleet operators who maintain multiple engine brands.
4. Onboard Displays / OEM Service Manuals
Some Cummins-powered equipment (e.g., generators, construction machinery, marine engines) includes a built-in display or OEM-provided monitoring system. These may show error codes directly on-screen along with simple fault descriptions. Additionally, OEM service manuals often provide fault code lists specific to the engine model, along with troubleshooting instructions.
Important Note: While multiple methods exist to retrieve codes, the final and most reliable reference should always be Cummins INSITE or the engine manufacturer’s official service manual, to avoid misinterpretation and unnecessary parts replacement.
Part 3. How Fault Codes Are Displayed (Quick Guide)?
Cummins fault codes appear mainly in two formats:
Traditional Numeric Codes (e.g., 212, 2962): Used in manuals and some tools, with descriptions and severity levels (advisory, derate, shutdown).
SPN/FMI Pairs (SAE J1939): SPN shows the parameter or sensor, FMI describes the failure type (e.g., high/low value, short circuit, communication fault).
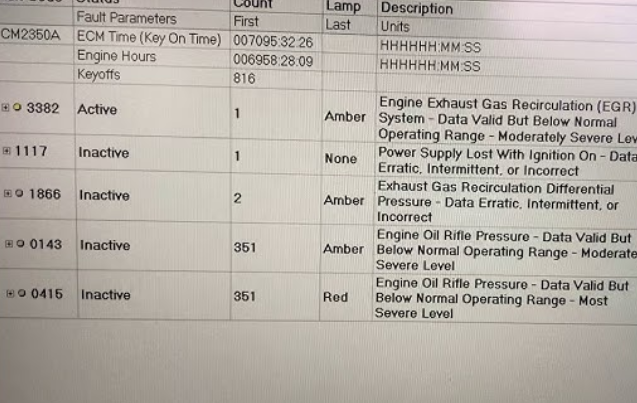
Additional info may include active/inactive status, freeze-frame data, timestamps, and severity indicators.
Note: Always use INSITE/FIS or the official service manual to interpret codes accurately, rather than relying on raw numbers alone.
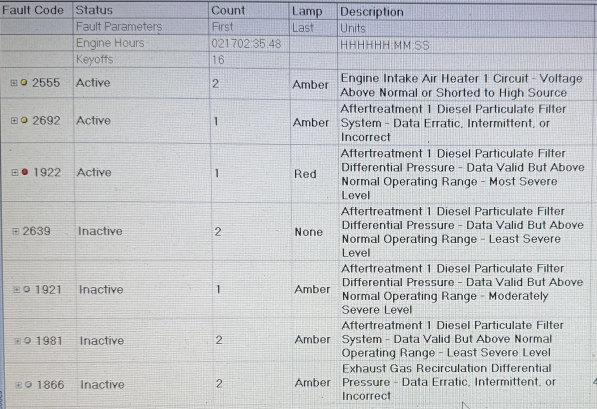
Part 4. Common Cummins Fault Codes
The following examples are based on frequently reported codes from Cummins documentation and industry sources. Since fault meanings may vary by engine model, ECM version, or software calibration, always verify with Cummins INSITE / FIS or the official service manual for your specific engine.
Fuel System
212 — Engine oil temperature sensor circuit abnormal (high voltage / short to high).
Possible checks/replacements: oil temperature sensor, wiring harness, ECM grounding.
259 — Fuel shutoff valve circuit stuck / abnormal open position.
Possible checks/replacements: fuel shutoff valve, control relay, driver wiring harness.
6254 / 6255 / 3712 (common on ISX / CM2350 series): Often emission/DEF-related or derate-related codes. Usually indicate “derate/secondary” issues.
Recommendation: Use INSITE to trace back to the root cause code and repair that first.
Intake / EGR / Exhaust
2962 — EGR temperature abnormal (higher than expected) — moderate/severe level.
Possible checks/replacements: EGR temperature sensor, EGR valve, related piping, or cooling system issues.
Sensors / Electrical
196 / 197 — Coolant level sensor voltage abnormal (too low / too high).
Check/replace: coolant level sensor, wiring, connectors.
221 / 222 — Barometric/atmospheric pressure sensor voltage abnormal (high / low).
Check/replace: barometric or turbo-related pressure sensors, intake piping for leaks.
234 — Engine overspeed (RPM exceeds protection limit).
Check: throttle operation, accelerator control, RPM sensor signal, or possible mechanical issues.
238 / 239 — Engine speed sensor supply voltage +5V abnormal (low / high).
Check/replace: speed sensor power circuit, sensor itself, ECM power supply.
241 / 242 — Vehicle speed signal lost or coolant level high-voltage warning.
Check: vehicle speed sensor, CAN/J1939 data link, wiring harness.
Injectors / Ignition / Cylinder
1553–1660 (series of codes): Injector driver circuit abnormal (different numbers correspond to individual cylinders, e.g., Cylinder #9, #12).
Check/replace: injector, injector driver module, wiring and connectors. (See Tier 4 / ISX fault code list for details.)
Data Link / Communication
426 — SAE J1939 data link communication failure (CAN bus interrupted/faulty).
Check: bus termination, cables, network devices, power supply, and ECM.
343 — ECM internal warning / hardware fault (requires INSITE for further diagnosis).
May require professional testing or ECM replacement/upgrade.
Misfire / Multi-Cylinder Faults (SPN Example)
SPN 1322 FMI 11 (or equivalent code) — Multiple cylinder misfire.
Check: fuel supply system, injectors, compression pressure, and ECM control logic.
Important Reminder:
The codes listed above are representative examples only and not exhaustive. Different Cummins engine families (B6.7, ISX, QSB, QSL, QSM, QSX, etc.) have their own extended code sets. The exact meaning and repair steps also vary by ECM version (e.g., CM2350, CM870) and emission tier/stage. Always confirm using INSITE, FIS, or the official service manual before troubleshooting or replacing parts.
Part 5. Step-by-Step Procedure to Read and Diagnose Fault Codes
Here’s a slightly more detailed, practical workflow you can follow when a Cummins engine shows a fault:
1. Record symptoms
- Note what you see and hear: Is the Check Engine lamp steady or flashing? Any power loss, smoke, abnormal noise, rough idle, or loss of performance?
- Record when it happens (hot/cold start, under load, at idle) and any recent events or repairs.
2. Use a diagnostic tool to read codes
- Connect Cummins INSITE or a capable J1939/OBD-II scanner. Read active, pending, and stored fault codes and capture the freeze-frame data (engine speed, load, temperatures, voltages at the time of the fault).
- If the scanner shows only derivative/derate codes, look for the root cause (primary) code that triggered them.
- Export or screenshot the results and save engine details (engine model, ECM part number, ECM software/calibration, VIN).
3. Look up codes in FIS / service manual
- Enter the code(s) in INSITE/FIS or the OEM manual to get the official trouble-tree, test procedures, wiring diagrams, and safety notes.
- Pay attention to severity (warning/derate/shutdown) and any special test equipment or precautions.
4. Perform the recommended checks (follow the trouble-tree)
- Electrical basics first: verify power and grounds, check for shorts/opens, inspect connectors and harnesses, and perform voltage/resistance checks per the manual.
- Signal checks: measure sensor outputs (voltage, frequency, resistance) and compare to expected ranges; use live data screens to observe signal behavior while varying engine conditions.
- Mechanical / subsystem checks: inspect fuel, EGR, turbo, cooling, or other related components as indicated.
- Avoid blind parts replacement: follow the FIS test steps—replace parts only after tests confirm the component is faulty.
5. Repair, clear codes, and verify
- Make the repair, clear the codes, and perform a road/test-load verification under the same conditions that originally produced the fault.
- Monitor live data and check that freeze-frame data no longer appears. If the fault recurs, capture the new freeze-frame and repeat diagnosis, working back through the trouble-tree.
- If diagnosis is inconclusive or points to ECM/software issues, consult Cummins support or an authorized service center for further analysis (ECM reflash/repair may be required).
6. Document and escalate when needed
- Keep a record of codes, freeze-frames, test results, replaced parts, and test-drive outcomes. This helps warranty claims and technical support.
- For complex or intermittent faults (communication errors, ECM internal faults), escalate to Cummins INSITE/FIS support or an experienced Cummins technician.
Safety reminder: follow all safety instructions in the service manual (isolate battery when required, beware of hot/pressurized systems, and use proper PPE).
Part 6. How to Select the Right Cummins Parts After Reading Fault Codes?
Selecting the correct Cummins parts is crucial for effective repairs and avoiding unnecessary replacements. This section explains how to select right Cummins parts after reading fault code.
Verify before replacing: Many faults are actually caused by wiring, grounding, or connector issues. Simply replacing a sensor may not resolve the root cause. Always follow the diagnostic steps—use a multimeter or oscilloscope to check circuits before swapping parts.
Match by original part number: Once you have the fault code and the recommended part number (PN) from INSITE, cross-check it carefully. Prioritize OEM (genuine) parts or high-quality verified alternatives from a trusted supply chain.
Consider ECM/software versions: In some cases, an ECM firmware update or parameter reconfiguration is required (for example, injector coding or sensor calibration). These adjustments typically need professional tools and manufacturer-level support.
Example: If the code indicates “Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit High,” first measure the sensor’s voltage/resistance. If the sensor itself is out of range, replace it with the correct PN oil temperature sensor. If voltage is abnormal, trace and test the +5V reference, ground, or ECM power supply circuit instead.

Part 7. Common Misconceptions and Key Considerations for Cummins Fault Codes
Understanding Cummins fault codes correctly can prevent unnecessary repairs and ensure effective troubleshooting. The following points summarize frequent mistakes and important reminders.
Avoid blind “parts swapping”
Never replace components without first checking the wiring and connections. Many faults are caused by harnesses, connectors, or relays rather than the sensors or actuators themselves.
Derivative codes vs. root cause codes
High-priority codes that trigger derate or shutdown are often derivative codes, meaning they result from another underlying fault. Always identify and fix the root cause code before addressing derivative faults.
Version and model differences
The same fault code may have slightly different meanings or required actions across engine models or ECM software versions. Always refer to Cummins INSITE/FIS or the official engine service manual for the specific engine in question.
Part 8. How Longshine Can Help for Cummins Fault Code?
Longshine is a trusted Cummins parts supplier, offering a wide range of genuine and high-quality components for various engine models. With years of experience, Longshine helps customers quickly find the right parts and ensures reliable engine performance.
Services & Advantages:
- Provides a full range of Cummins parts, including engine components, electronic modules, fuel system parts, sensors, and filters.
- A professional team assists customers in matching the correct parts.
- Factory-direct supply helps reduce procurement costs.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly reading Cummins fault codes is the first and most critical step in maintaining and repairing your engine. Accurate interpretation allows you to identify the root cause of issues, select the appropriate Cummins parts, and ultimately extend the life and reliability of your engine.
If you need assistance decoding fault codes or sourcing reliable Cummins parts, our team at Longshine is ready to help. With our professional support and full range of quality components, you can resolve issues faster, reduce downtime, and ensure your engine performs at its best.
