How Many Miles Will a 6.7 Cummins Last?
The 6.7L Cummins diesel engine is known for its durability and performance and is used in Ram trucks, industrial engines, and generator sets. It enjoys industry acclaim for low running costs, high reliability, and engine output.
However, for most owners and users, the most common question is how long will a 6.7 Cummins last?
Understanding the real lifespan of the engine not only affects overall operating costs but also helps make smarter decisions when it comes to maintenance, resale, and parts replacement.
Part 1. Average Estimated Lifespan of the 6.7 Cummins Engine
When properly maintained, the 6.7 Cummins diesel engine is known for its impressive longevity. On average, it can last between 350,000 to 500,000 miles, and many owners have reported engines running smoothly even beyond 600,000 miles with consistent care.
This exceptional durability stems from Cummins’ robust engineering philosophy, which emphasizes strength, precision, and reliability:
- High-strength cast-iron engine block and forged steel crankshaft: These heavy-duty components are designed to withstand extreme pressure and thermal stress, ensuring long-term mechanical stability even under heavy towing or industrial workloads.
- Advanced fuel injection system: The precise electronic fuel delivery improves combustion efficiency, reduces wear, and enhances both power and fuel economy.
- Efficient cooling and lubrication system: Optimized oil flow and temperature regulation prevent overheating and component friction, which are common causes of engine wear.
However, here you should also note that the actual lifespan of a 6.7 Cummins engine isn’t fixed. It can vary significantly depending on factors such as maintenance habits, driving conditions, load capacity, and fuel quality.
Engines used for consistent heavy hauling or operated in harsh environments may wear out sooner, while those maintained regularly and driven under moderate conditions can easily surpass the expected mileage range.

Part 2. Factors That Affect How Long a 6.7 Cummins Engine Will Last
1. Regularity and Quality of Maintenance
Regularly scheduled upkeep is paramount to prolonging the lifespan of the engine. Recommended practices are below:
- Change the engine oil and oil filter every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, as specified in the owner’s manual.
- Replace the fuel and air filters as per the Cummins schedule.
- Review the coolant level and condition, engine aspirating/discharge belts, hoses, and fuel-injecting system and the drive belts at scheduled intervals.
- Use Cummins genuine parts, filters, and systems of other reputable manufacturers.
Why this is important: Failing to complete oil changes in a timely manner accelerates internal wear and sludge buildup. Fuel contamination and clogged fuel injectors create poor combustion and accelerate cylinder abrasion. Collectively, these issues fuel a deterioration of engine lifespan.
2. Load Conditions and Driving Behavior
Engine usage patterns influence the wear and tear it experiences and, subsequently, engine lifespan.
- Any sustained, long-distance, and steady travel of the vehicle on freeways is less damaging and lowers the engine wear than the stop-and-go system of urban travel.
- Frequent and strenuous towing, constant, fully loaded, and short-distance travel of the vehicle, and cyclic operation of empty and fully loaded structures increase thermodynamic pressure, mechanical fatigue, and enhance wear and tear of engine parts.
- Excessive periods of idling promote a combustion condition of the engine, create low and stagnant down flow of combustion gases, injectors fouling with carbon deposits, clogging the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, and promoting rapid oil deterioration.
Engine wear and tear is countered by minimizing overloading, persistent idling, and engine operation under extreme conditions and with frozen loads.
3. Diesel and Lubricant Quality
An increased likelihood of untimely breakdown also occurs due to poor diesel quality and wrong diesel lubricant selection.
- The use of quality diesels that are low in sulfur will also mitigate deposit formation and protective aftertreatment system failures.
- Use engine oils that satisfy the API CJ-4 (or a more current version) and respective Cummins oil viscosity recommendations.
- Do not postpone oil changes, and do not mix the oils.
Fuel and oil that are of poor quality do not provide adequate protection and lead to increased wear within the rings and bearings. Combustion problems and injector fouling are results of low-quality and contaminated fuel.
4. Operating and Environmental Constraints
Service life will be shortened in unattended cases.
- The presence of extremely high temperatures, low temperatures, heavy dust, and corrosion will all lead to advanced wear.
- Dusty situations will require more frequent inspection and replacement of air filter elements and pre-filters. Cold situations will require the use of correct cold-grade oils, and block heaters may be required.
- For engines that endure continuous heavy-duty and extreme operational conditions, do not only shorten planned maintenance intervals but also increase the frequency of inspection as well as the air, fuel, and cooling systems.
Obvious neglect and harsh use will materially reduce the engine’s service life. The expected life of 6.7 liters in a Cummins engine will be achieved when the owner practices reasonable operating habits along with punctual maintenance of high quality.
Part 3. Common Signs of Aging in the 6.7 Cummins Engine
As mileage grows higher, the 6.7 Cummins engine will start to wear down as well as the performance drop. These issues can be fixed before they escalate to more serious issues.
Hard Starting or Knocking Noise
Symptoms: engine starts hard (especially cold or hot), requires more than 1 ignition attempt, or makes rhythmic metallic knocking noise after the engine is turned on.
Possible Reason: Worn piston rings, unequally sized bearing clearances, faulty injectors, incorrectly set injection timing, low oil pressure.
Recommended Tests: Do compression and oil pressure test, check and set injectors timing, check for bearing wear on main and connecting rods, and check for piston rings to be worn and scored.
Increased Fuel or Oil Consumption
Symptoms: Increase of engine oil and fuel consumption at a normal driving condition.
Possible Reasons: Worn piston rings, damaged valve seals which means chamber oil combustion, turbo seals damaged, and fuel system issue leading to poor combustion.
Recommended Tests: Do a compression and leak down test, check turbo seals and pcv crankcase ventilation system, and analyze the fuel injection and combustion.
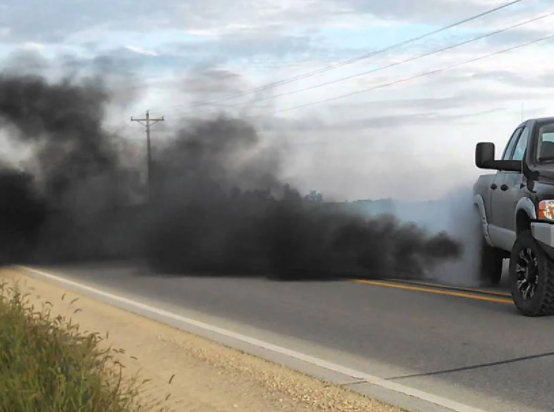
Excessive Black or Blue Smoke from the Exhaust
Symptoms: Thick black smoke under acceleration or heavy load (unburned fuel), or blue smoke indicating oil burning.
Possible Causes:
- Black smoke: Overfueling, leaking injectors, or restricted air intake.
- Blue smoke: Oil entering the combustion chamber through worn piston rings, valve seals, or turbo seals.
Recommended Checks: Calibrate and test injectors for leaks, check air filters and boost system, inspect turbo and valve guide seals, and monitor oil level and consumption pattern.

Loss of Power or Sluggish Acceleration
Symptoms: The engine feels weak under load, acceleration is delayed, and low-end torque is reduced.
Possible Causes: Restricted air or fuel supply, worn turbocharger components, clogged EGR or intake system, or poor injector atomization.
Recommended Checks: Inspect air intake and boost pressure, examine turbocharger blades and bearings, check injector flow and spray quality, and verify valve timing.
Recurring Check Engine Light or DTCs
Symptoms: The MIL turns on and off frequently and/or DTCs P0xxx/P2xxx are logged or active.
Possible Causes: Aging sensors (oil pressure, intake temperature, and/or pressure), fuel system problems, ECM problems, mechanical problems, and/or fault protective mode genuine issues.
Recommended Actions: Analyze logged fault codes, check sensors and their associated wiring, check oil and fuel pressure, and assess other possible parameters of the cooling system.
Recommended Overall Action Plan
All the previously mentioned 6.7 Cummins engine problems, associated with the possible component diagnostics, require a full engine diagnostic scan. This should include code readings, compression/leak-down tests, and fuel and oil system checks. The engine will run longer and save more money on engine repairs and breakdowns if worn-out components are replaced quickly.
Part 4. How to Extend the Service Life of a 6.7 Cummins
Avoiding the 500,000-mile mark on the 6.7 Cummins is impossible when the correct use and maintenance is given. Here are a few to get you on the right track:
- Follow manufacturer oil and filter intervals exactly — fresh oil and clean filters are the single most effective way to reduce wear.
- Clean the fuel system – injectors and quality diesel fuel, with approved fuel additives to reduce injector deposits and promote efficient combustion, will clean and help maintain a fuel system.
- Intake and EGR systems – routine maintenance of these will mitigate the need to clean the systems of carbon buildup that will rob the engine of power and increase the strain on it.
- Use genuine replacement parts – injectors, turbos, starters and filters all sourced from reputable contenders will mitigate the risk of failure from using unbranded aftermarket parts.
- Avoid frequent cold starts and chronic overloading — allow the engine to reach operating temperature before heavy work, and don’t habitually run above rated loads.
As a professional Cummins parts supplier, Longshine offers genuine and a full range of Cummins parts that help keep your engine operating reliably at every stage of its life.

Part 5. Key Component Maintenance Recommendations at Different Mileage Stages
As the 6.7 Cummins engine accumulates mileage, certain critical components face increased wear and tear. Performing targeted inspections and maintenance at specific mileage intervals can help prevent major failures, maintain engine performance, and extend overall service life.
The following table outlines recommended maintenance for each mileage stage:
| Mileage | Recommended Maintenance | Purpose |
| 100,000–150,000 miles | Replace fuel filter, water pump | Maintain stable fuel delivery and cooling system performance, preventing early wear and overheating |
| 200,000–300,000 miles | Inspect turbocharger and injectors | Prevent power loss, reduced fuel efficiency, and abnormal turbo wear |
| Over 400,000 miles | Inspect head gasket, engine mounts, starter | Prevent structural damage and starting issues caused by aging |
| Over 500,000 miles | Full engine inspection or rebuild | Thoroughly check and replace core components as needed to ensure extended engine life |
Conclusion: Key to Maintaining Your 6.7 Cummins
In the diesel engine world, 6.7 Cummins engine has become a standard model to determine quality engine durability. With good maintenance, quality of the diesel fuel, reliable and generous preferring replacement parts, it can reliable serve over 500k miles.
Stability of operation over time requires a reliable parts supplier.
Longshine, as a reliable distributor of Cummins engines and parts, provides guests genuine parts of the highest quality. This has greatly assisted customers engine life maintenance cost and performance consistency.
Want to learn more about 6.7 Cummins parts? Contact Longshine today to provide your engine with the most reliable support.
